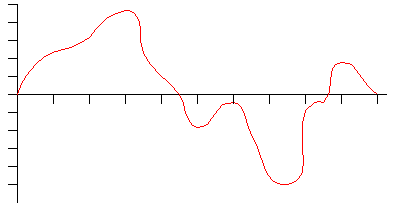
Sound can be visually represented on a graph as waves. By comparing this wave to the graphics below, you can easily see how digital sampling processes sound data.
Which is better,
Before we jump into the argument, we should take a quick look at what makes a sound digital or analog. It all has to do with how you
Digital media includes
Today, advances in analog-to-digital conversion methods have improved the quality of digital recordings. Some people say that high sampling rates and increased precision have erased any distinction between digital and analog. Others disagree -- sometimes passionately. There's a sizeable population of
What are the differences in the actual sound of analog and digital recordings? Keep reading to find out.
(Source: Jonathan Strickland,HowStuffWorks.com)