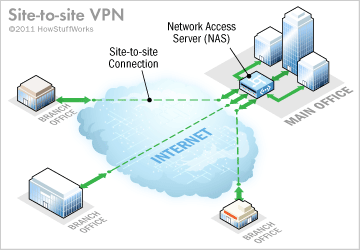
A site-to-site VPN connection lets branch offices use the Internet as a conduit for accessing the main office's intranet.
A
There are two types of site-to-site VPNs:
- Intranet-based -- If a company has one or more remote locations that they wish to join in a single private network, they can create an intranet VPN to connect each separate LAN to a single WAN.
- Extranet-based -- When a company has a close relationship with another company (such as a partner, supplier or customer), it can build an extranet VPN that connects those companies' LANs. This extranet VPN allows the companies to work together in a secure, shared network environment while preventing access to their separate
intranets.
Even though the purpose of a site-to-site VPN is different from that of a remote-access VPN, it could use some of the same software and equipment. Ideally, though, a site-to-site VPN should eliminate the need for each computer to run VPN client software as if it were on a remote-access VPN. Dedicated VPN client equipment, described later in this article, can accomplish this goal in a site-to-site VPN.
Now that you know the two types of VPNs, let's look at how your data is kept secure as it travels across a VPN.


