Mobile nodes such as autonomous underwater vehicles are flexible to carry out large-scale underwater detection. But when they access the underwater wireless acoustic network composed of static nodes for uplink transmission, the collision in the network will be intensified and the data transmission among static nodes will be interrupted.
To ensure the timely access of the mobile node without disturbing the data packets transmission of static nodes, researchers from the Institute of Acoustics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IACAS) proposed a Sequence-scheduled and Query-based medium access control (MAC) MAC protocol for underwater acoustic networks with a mobile node. The proposed protocol achieved higher throughput of static nodes and lower mobile access delay.
Researchers analyzed the collision of control packets during the handshake interaction phase, and proposed an adjustment mechanism for the transmission order of control packets to achieve a successful reservation of static nodes. After the handshake, the receiver switched to either of the two schemes named ORDER and QUERY/START according to whether it had received the access request of the mobile node. By the active query of QUERY, researchers assigned the mobile node a higher priority to access the network timely. Finally, they transformed the transmission sequence of data packets into a traveling salesman problem and applied the maximum and minimum ant colony algorithm to determine the sequence scheduling.
Simulations showed that, compared to two reference protocols, the maximum nodal throughput of the proposed MAC protocol increased at least 20%, while the access delay of the mobile node decreased by up to 90%. Besides, the average access probability of the mobile node in the proposed protocol was more than 90%.
This research provides a feasible way to realize the collision-free and timely access of a mobile node to the network to complete the uplink transmission. Researchers will further study the efficient access scheme of multiple mobile nodes.
The research, published online in the Journal of Communications and Information Networks, was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2018YFC1405904).
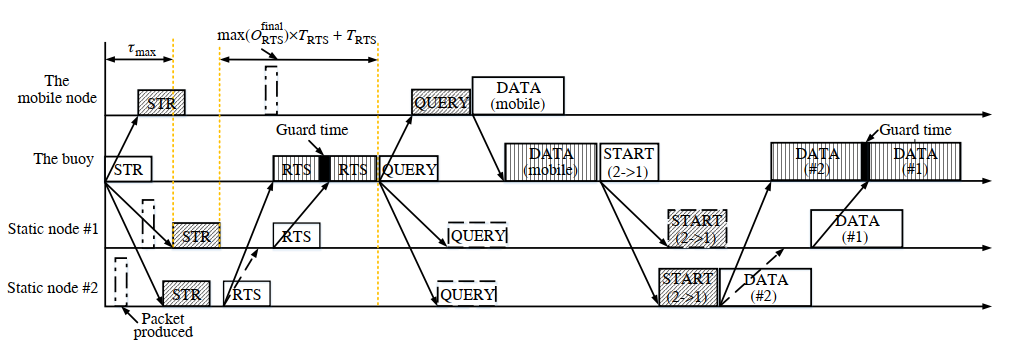
Figure 1. Sequence diagram of the proposed protocol. (Image by IACAS)

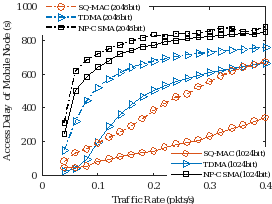
Figure 2. Nodal throughput of static nodes (the left) and Access delay of the mobile node (the right). (Image by IACAS)
Reference:
HUANG Jing, CHI Cheng, WANG Wei, HUANG Haining. A Sequence-Scheduled and Query-Based MAC Protocol for Underwater Acoustic Networks with a Mobile Node. Journal of Communications and Information Networks, June 2020, 5(2): 150-159. DOI: 10.23919/JCIN.2020.9130431.
Contact:
ZHOU Wenjia
Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100190 Beijing, China
E-mail: media@mail.ioa.ac.cn


