The end-to-end speech recognition directly convert the speech signal to text by deep learning models, among which the models based on attention mechanisms achieve higher recognition accuracy. However, most attention models require full speech, and are unsuitable to process the speech stream.
Aiming at the application scenarios of online speech recognition, researchers from the Institute of Acoustics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IACAS) studied the performance of mainstream attention mechanisms when processing the speech stream. They proposed an online attention mechanism by monotonically truncating the speech stream and an efficient decoding algorithm.
Researchers analyzed the property of the attention weight distribution at each speech frame in the speech recognition system. They pointed out that the attention weights of existing online attentions decayed exponentially, which were unsuitable for long-form speech. They also found that the mismatch between training and inference caused the performance degradation. Based on the issues mentioned above, researchers designed the monotonically truncated attention to improve the property of the exponential decay of attention weights and narrow the gap between training and inference by discretizing attention weights.
Conducted on the public Chinese and English speech recognition corpus, researchers demonstrated that the monotonically truncated attention model was more stable for the long-form speech. Based on the joint attention and Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) decoding algorithm, the character error rate of the online ASR system was slightly higher than that of the offline system. However, it was around 1.5 times faster in terms of decoding speed.
This work provides a feasible solution for the end-to-end speech recognition technology to be implemented in large-scale industrial online products.
The research, published online in IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.11590774, 11590772, 11590770).
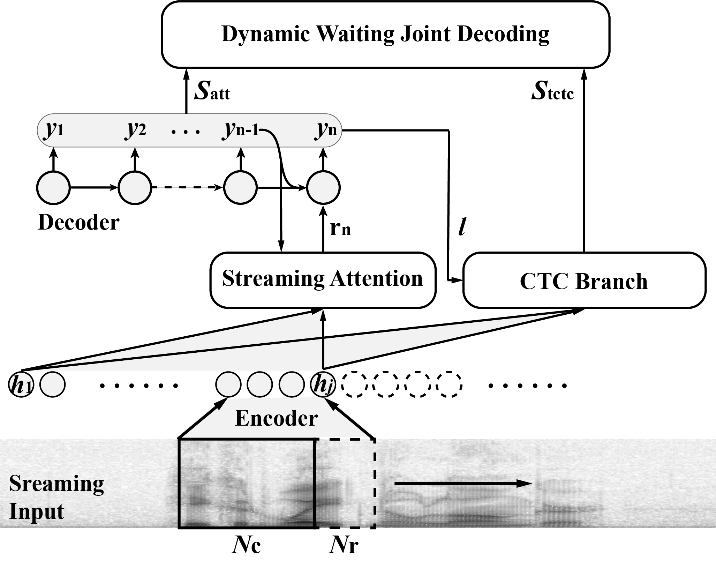
Online end-to-end ASR architecture. (Image by IACAS)
Reference:
MIAO Haoran, CHENG Gaofeng, ZHANG Pengyuan, YAN Yonghong, Online Hybrid CTC/Attention End-to-End Automatic Speech Recognition Architecture. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, vol. 28, pp. 1452-1465, 2020, DOI: 10.1109/TASLP.2020.2987752.
Contact:
ZHOU Wenjia
Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100190 Beijing, China
E-mail: media@mail.ioa.ac.cn


