When implementing functions like data fusion, power management and transmission scheduling, in underwater wireless sensor networks (UWSNs), it is required that all the nodes share a common reference of time. Consequently, time synchronization is a prerequisite and a crucial support technique for UWSNs.
Energy consumption and accuracy are two essential factors for designing a synchronization protocol. To cope with these factors, researchers from the Institute of Acoustics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IACAS) proposed a three-step receiver-only-based time synchronization protocol for UWSNs, which was energy-efficient with high synchronization accuracy.
Adopted the receiver-only-synchronization scheme, researchers used the silent nodes (the nodes that could only receive messages) in the UWSN to overhear a pair of active nodes (the nodes that could both send and receive messages) and performed two-way timing message exchanges. This kind of scheme reduced the amount of message-exchanges among nodes.
Specifically, in the proposed protocol, researchers used support vector machine to estimate the clock skew on the active node, and then calculated the maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) of the clock skew on the silent node (without using CVX toolboxes) and a minimum variance unbiased estimation of the offsets on both active and silent nodes.
The results showed that the proposed protocol had lower energy consumption and higher synchronization accuracy than other existing protocols such as LDA, JMLE, and GMLLE.
Taking both energy consumption and synchronization accuracy into account, the proposed synchronization protocol for UWSNs is suitable for UWSNs and has a good application prospect.
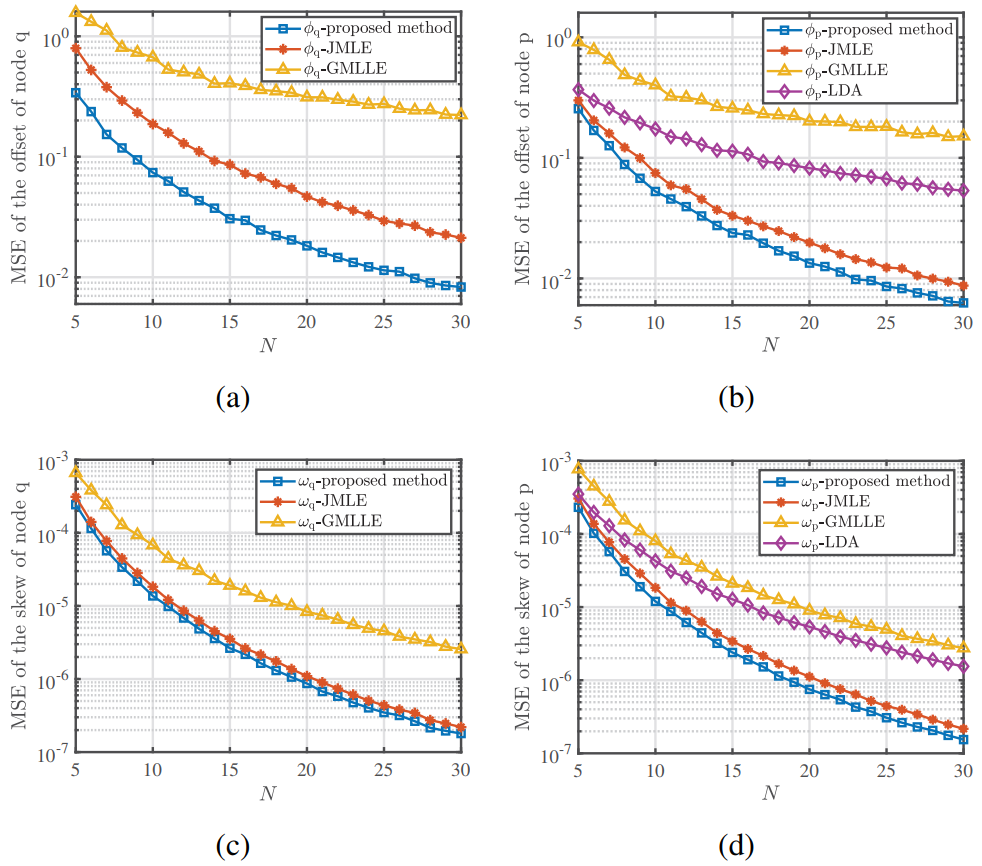
Figure 1. Mean square error of synchronization without mismatches. (Image by IACAS)
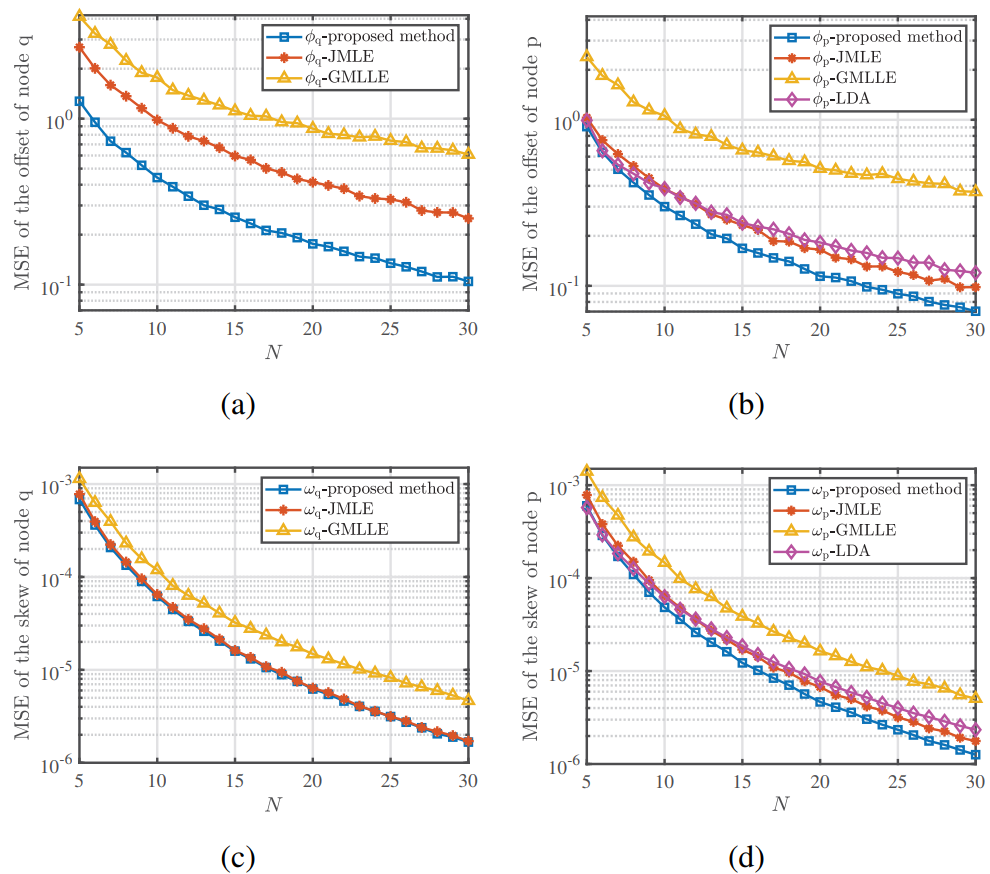
Figure 2. Mean square error of synchronization in the case of mismatches. (Image by IACAS)
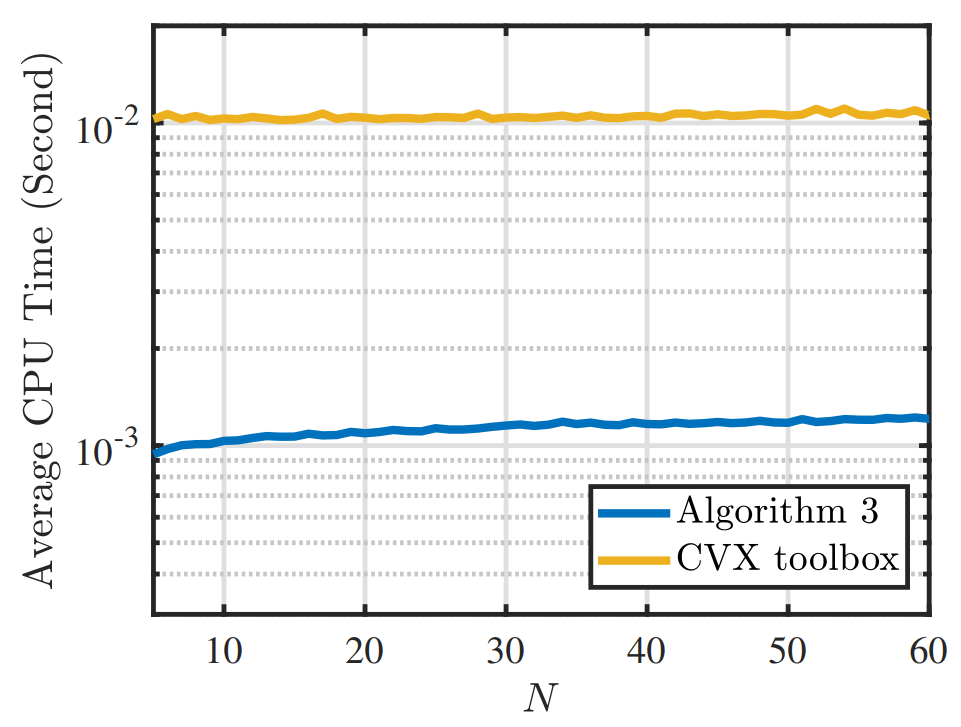
Figure 3. Average CPU time of the proposed MLE algorithm (Algorithm 3) and the MLE algorithm using CVX toolboxes. (Image by IACAS)
The research, published online in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61725106, 61901467).
Reference:
LIU Guopeng, YAN Shefeng, MAO Linlin. Receiver-only-based time synchronization under exponential delays in underwater wireless sensor networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020. DOI: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2988695.
Contact:
ZHOU Wenjia
Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100190 Beijing, China
E-mail: media@mail.ioa.ac.cn


