In a real-room environment, there might be many people talking at the same time with background noise. This is known as the cocktail party problem. The goal of blind source separation (BSS) is to estimate the source signals from their mixtures without any prior information about the sources and the mixing processing. However, the computational complexity of many BSS methods is too high to be used in the practical application.
In order to reduce the computational complexity of the blind source separation method, researchers from the Institute of Acoustics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IACAS) presented a low-complexity permutation alignment method based on the inter-frequency dependence of signal power ratio.
The relevant research results were recently published in the international academic journal Speech Communication.
The frequency-domain independent component analysis (ICA) approach has been extensively investigated among all BSS methods. However, it leads to the well-known permutation problem because the separation is performed in each frequency bin independently.
To address this problem with low complexity, researchers employed the inter-frequency correlation as an effective measurement to align the permutations. The proposed permutation alignment approach included a local optimization and a fine global optimization. The local optimization was based on the bin-wise permutation and further followed by a local centroid correction, which could prevent the misalignment spread effectively. The researchers finally employed a fine global optimization to correct the permutation and improve the robustness.
Computer simulations demonstrated that the proposed method achieved a comparable separation performance with the state-of-the-art permutation alignment algorithms. The complexity of the proposed method was much lower especially as the number of sources increased.
This low-complexity blind source separation method could be used in speech recognition, telephone communication and hearing aid devices to improve speech quality and speech intelligibility.
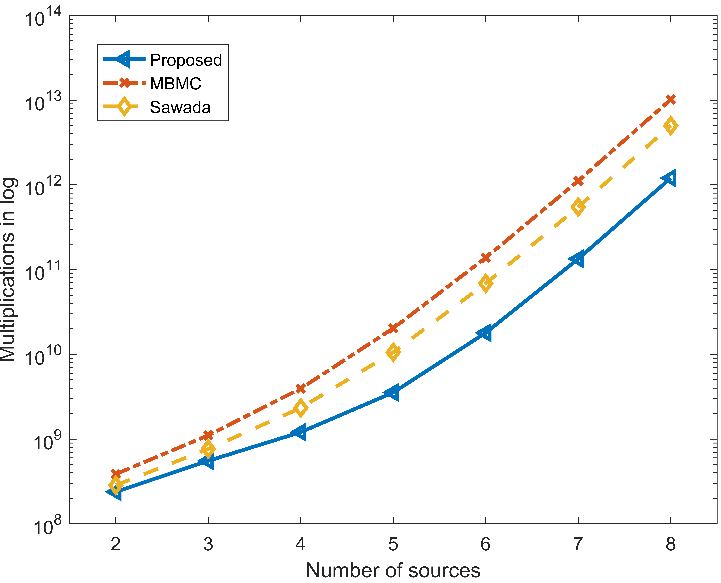
Figure 1. Computational complexity comparison. (Image by IOA)
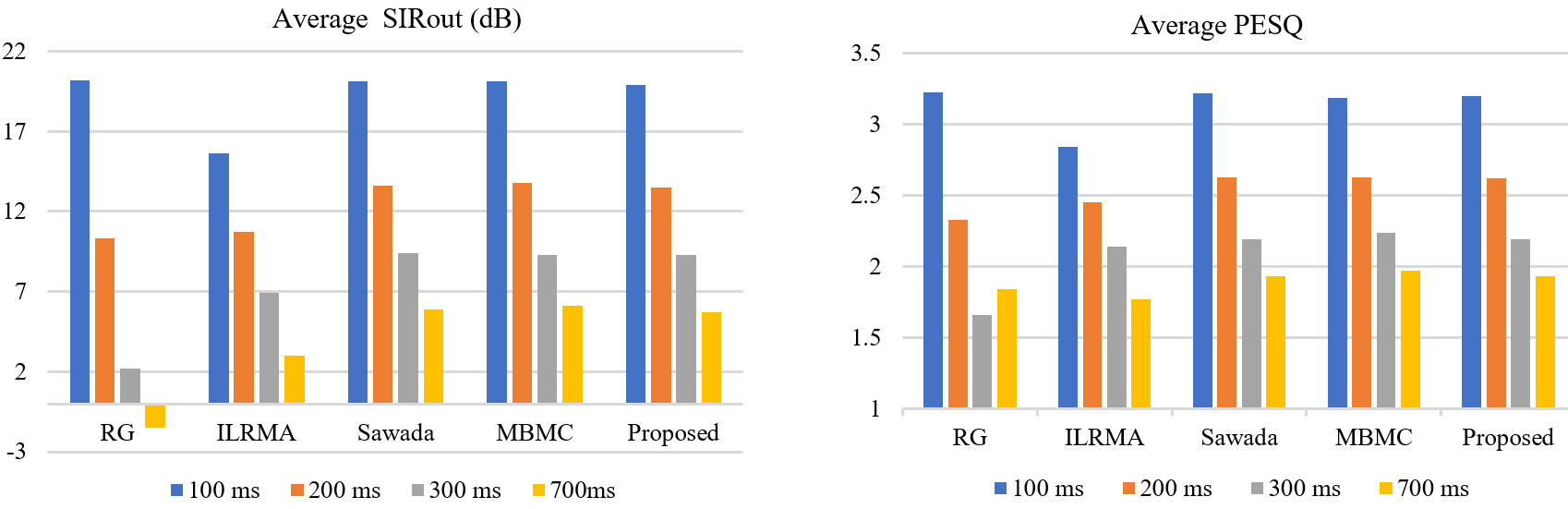
Figure 2. Separation performance of five algorithms with different reverberation times, (left) average SIRout (dB) and (right) average PESQ. (Image by IOA)
The research was supported by National Key R & D Program of China under Grant 2017YFC0804900, Youth Innovation Promotion Association of Chinese Academy of Sciences under Grant 2018027, IACAS Young Elite Researcher Project QNYC201812 and the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences under Grant no. XDC02020400.
Reference:
KANG Fang, YANG Feiran, YANG Jun. A low-complexity permutation alignment method for frequency-domain blind source separation. Speech Communication. 2019, 115: 88-94. DOI: 10.1016/j.specom.2019.11.002
Contact:
ZHOU Wenjia
Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100190 Beijing, China
E-mail: media@mail.ioa.ac.cn


