Utilizing ultrasound waves to detect and image defects in materials non-destructively is the most important NDT technique in industrial field. With the development of automatic industrialization, real-time imaging now becomes a critical problem for ultrasonic testing methodology.
Total Focusing Method (TFM), a super ultrasonic phased array imaging algorithm, is described as the “Gold Standard” due to its high testing resolution and sensitivity for defects in metals and other materials.
From a long time, TFM can only be achieved offline owing to the huge amount of data acquisition and computation requirements. Computing platform such as Graphic Process Unit (GPU) was suggested to implement the TFM algorithm. However, limited by parallel performance and transfer bottleneck of raw data, a real-time TFM testing still cannot be obtained.
Aiming to meet the need of real-time applications, WANG Chong, a doctoral student from the Institute of Acoustics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, along with his mentors Prof. WANG Xiaomin and three other researchers, designed an advanced parallel architecture in Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) to make ultrasonic Total Focusing Method (TFM) a real-time Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) technique, a significant and promising acceleration for TFM so far.
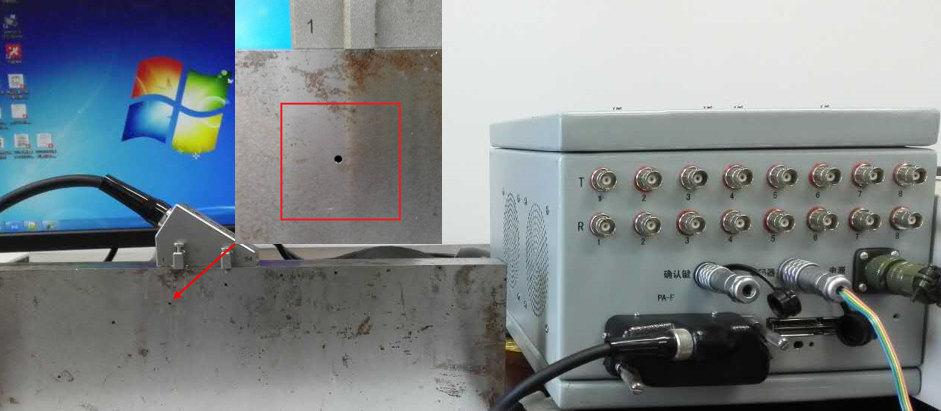

Figure 1. Phased Array system designed in Research Center for Ultrasonics and Technologies (Image by WANG Chong)
Researchers developed a specific parallel architecture in FPGA for the TFM algorithm. Multiple imaging pixels in the TFM testing image could be calculated simultaneously to reduce the total computation time. Utilizing the DSP resources in FPGA, filters and Hilbert transform could be applied at the same time to improve the image quality without any extra time cost. The whole TFM algorithm can be calculated inside FPGA and only the image result was transferred up to CPU for display.
With simplified system design and reduced transfer bandwidth, the TFM imaging efficiency is 4.3 times faster than other strategies in the same testing situation.
The proposed FPGA architecture has shown good performance in experimental results in different testing situations. In tests, a side-drilled hole in steel block was used as the defect, image was formed with the efficiency achieved as high as 312.5Hz. The high TFM efficiency remains stable when the testing area became larger and the image pixels increased.
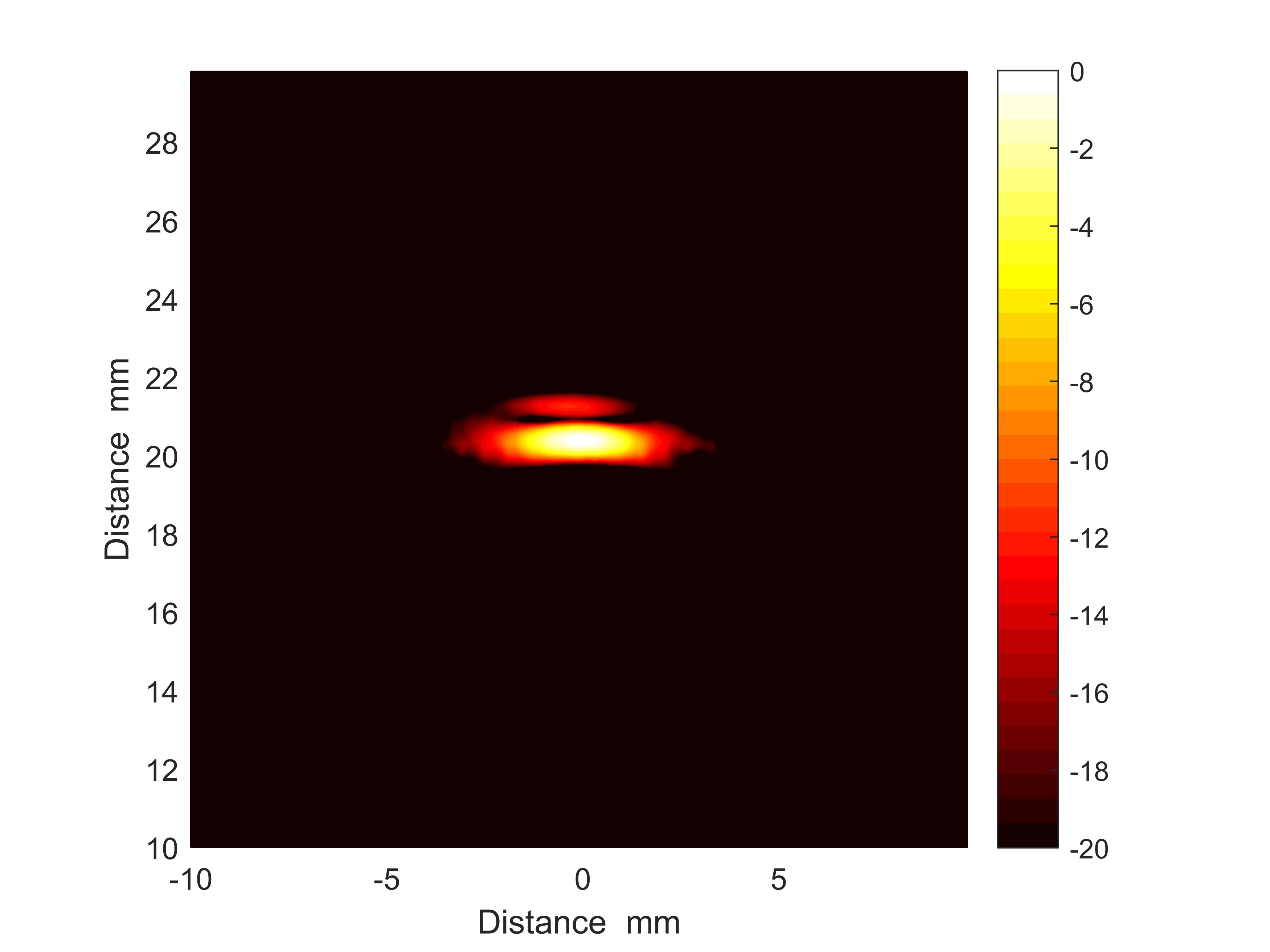
Figure 2. TFM image of side drilled hole calculated in FPGA (Image by WANG Chong)
This research makes it possible for the automatic real-time TFM testing applications in industrial fields.
The paper entitled “Efficient Acceleration for Total Focusing Method Based on Advanced Parallel Computing in FPGA” was published on The International Journal of Acoustics and Vibration.
Researchers have applied for a patent for this work.
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Scientific Research and Equipment Development Project of CAS.
Reference:
WANG Chong, MAO Jie, LENG Tao, ZHUANG Zeyu, WANG Xiaomin. Efficient Acceleration for Total Focusing Method Based on Advanced Parallel Computing in FPGA. The International Journal of Acoustics and Vibration, Volum: 22, Number: 4(2017). DOI:10.20855/ijav.2017.22.4500.
Contact:
WANG Rongquan
Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100190, Beijing, China
Email: wangrongquan@mail.ioa.ac.cn


