In the parametric loudspeaker, the accurate measurement of the difference-frequency sound is vital for understanding the principle of the parametric array, and is also important for the practical design in audio engineering.
However, it is not that easy to do that, especially in the nearfield or near the beam axis. The actual cause is the spurious signal generated as a result of nonlinearity at the receiving system, originated by the finite-amplitude ultrasonic waves (referred as the primary waves).
To solve this problem, researchers JI Peifeng, HU Wenlin and YANG Jun from the Key Laboratory of Noise and Vibration Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences propose an acoustic filter using phononic crystals to suppress the primary waves without significantly affecting the difference-frequency sound. The proposed filter demonstrates good performance to reduce the spurious signal in the measurement of the parametric loudspeaker for both the axial propagation and the directivity measurement.
The phononic crystals, synthetic materials that are formed by periodic variation of the acoustic properties of the material (i.e., elasticity and mass) have attracted considerable interest during the last two decades. One of the main properties of the phononic crystals is the possibility of having a phononic band gap, over which there can be no propagation of elastic waves in the structure. The existence of the band gap gives these artificial materials potential applications such as the filtering of elastic waves.
An acoustic filter using phononic crystals, consisting of 5×7 cylinders, has been prototyped as shown in the inset of Fig. 1. The material of the cylinder is aluminum alloy. The filter has the dimension of 29.2 mm × 30.2 mm × 20 mm in total, which can be easily mounted in front of the microphone.
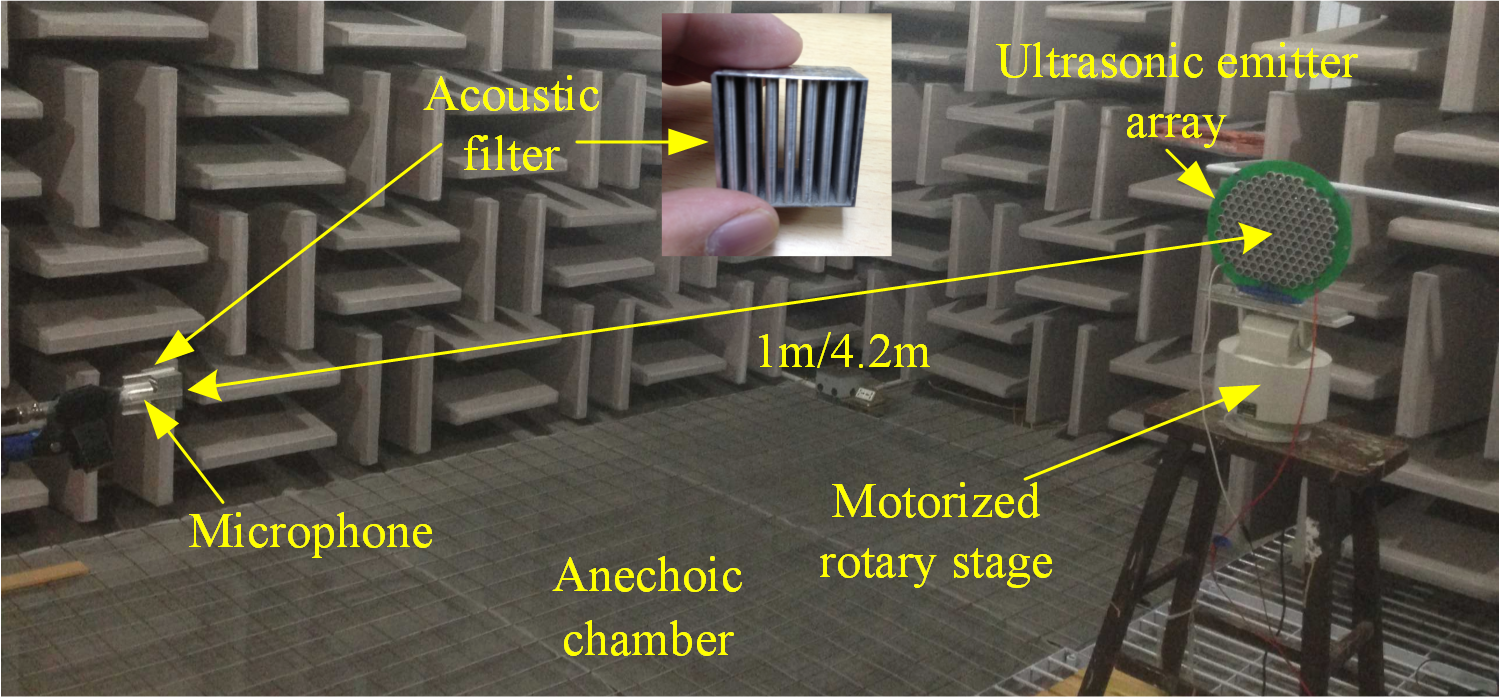
Fig.1 Experimental setup (Image by JI)
A preliminary experiment to examine the performance of the proposed filter is carried out in the anechoic chamber of the Institute of Acoustics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the experimental setup is illustrated in Fig. 1.
The normalized frequency responses of parametric loudspeaker measured without and with the acoustic filter for both two distances are illustrated in Fig. 2, where the effect of the ultrasonic emitter array has been removed. The audible sound generated by parametric loudspeaker is proportional to 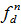 , where
, where 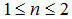 .
.
As shown in Fig. 2, the experimental results indicate 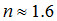 , which is a good approximation of the difference-frequency dependence. The normalized numerical results both at 1 m and 4.2 m based on the Gaussian-beam expansion technique are also plotted in Fig.2 and almost fit with the curve of
, which is a good approximation of the difference-frequency dependence. The normalized numerical results both at 1 m and 4.2 m based on the Gaussian-beam expansion technique are also plotted in Fig.2 and almost fit with the curve of 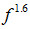 .
.
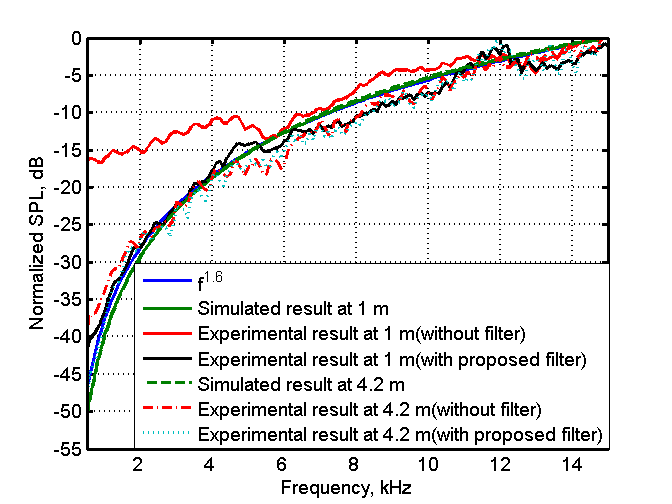
Fig. 2 Normalized frequency responses of the difference-frequency signal for parametric loudspeaker at 1 m and 4.2 m (Image by JI)
In order to evaluate the performance of the proposed filter in the directivity measurement of the parametric loudspeaker, another experiment is also carried out. And the measured frequency responses of the difference-frequency signal are shown in Fig. 3 for six different angles.
From this figure, it is noted that in this research, the acoustic filter is still effective in the directivity measurement, and when the rotating angle is larger than 7.5°, no acoustic filter is necessarily needed.
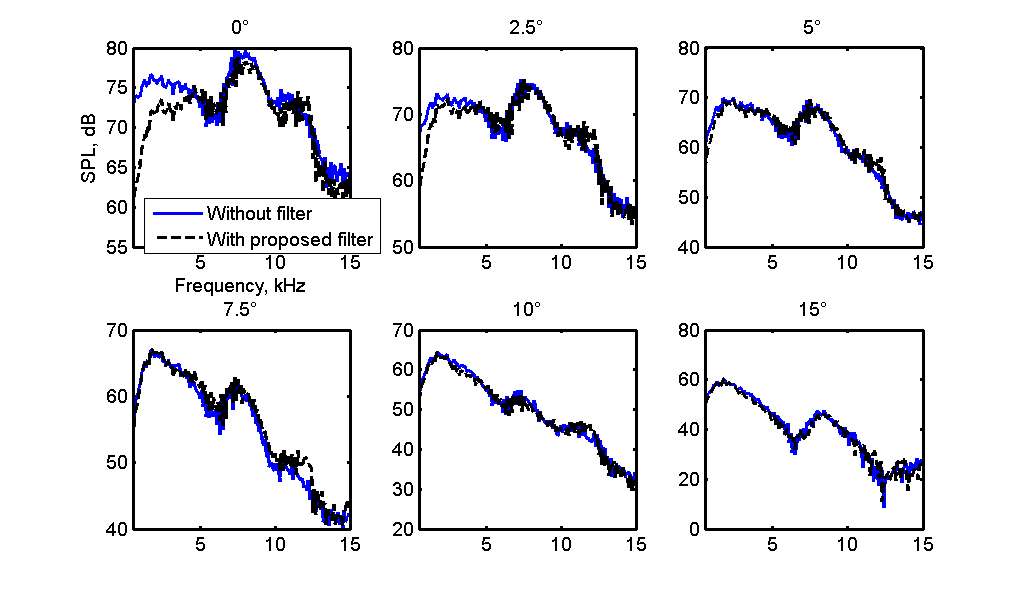
Fig. 3 Measured frequency responses of the difference-frequency signal with different angles for parametric loudspeaker (Image by JI)
Both simulations and experiments are carried out to verify the performance of the proposed acoustic filter using phononic crystals. It proves that the filter can eliminate the spurious signal in the measurement of the parametric loudspeaker by suppressing the levels of the primary waves without significantly affecting the levels of the audible sound.
Funding for this research came from National Natural Science Fund of China under Grant Nos. 11174317 and 11304349, and Youth Innovation Promotion Association of Chinese Academy of Sciences (2015019).
Reference:
JI Peifeng, HU Wenlin, YANG Jun. Development of an Acoustic Filter for Parametric Loudspeaker Using Phononic Crystals. Ultrasonics (vol. 67, pp. 160-167, April 2016). DOI: 10.1016/j.ultras.2016.01.013
Contact:
JI Peifeng
Key Laboratory of Noise and Vibration Research, Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100190 Beijing, China
Email: jipeifeng@mail.ioa.ac.cn


