The gunshots detection is of topical interest in areas related to anti-terrorism, public security and military actions. Its methods are based on the detection of acoustical gunshot signatures, including muzzle blast and shock wave.
The shock wave is an N-shaped wave emanating in the form of an acoustic cone trailing the projectile. As a distinguishable signature of acoustical gunshot signal, the shock wave has been widely used for gunshot detection.
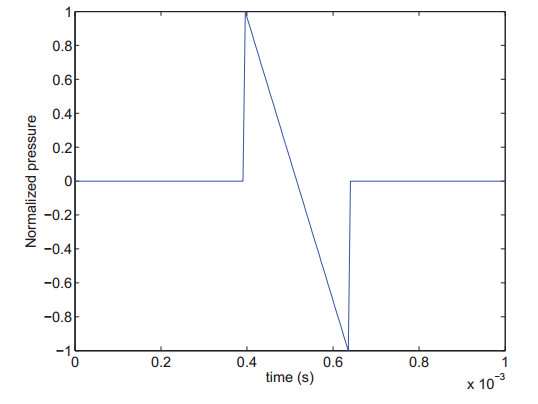
Fig. 1 Simulated ideal shock wave (Image by XIE).
A multi-scale product (MSP) detector based on discrete wavelet transform is the most popular detector in shock wave detection. This approach enhances multi-scale peaks due to edges, while suppressing noise, by exploiting the multi-scale correlation due to the presence of the desired signal in a direct way. It has low computational complexity and robust with unknown interference. However, since the method doesn’t consider the distribution of the noise, the performance decreases at low signal-to noise ratio (SNR).
To address this problem, researchers from the Institute of Acoustics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering of the Ryerson University (Toronto) formulate the shock wave detection problem as a detection problem in the time-scale domain.
They present a theoretical analysis of the MSP method. It shows that the MSP method is optimal in likelihood ratio sense only when it is assumed that the coefficients follow log-normal distribution with some assumptions of the mean and the variance. Based on the analysis, a general condition is considered. An optimal detector based on log-normal distribution under the standard likelihood ratio test is proposed.
The implementation of the detector is based on estimation of the probability density function parameters. In order to estimate the parameters more accurately, the coefficients corresponding are separated to the edge form the observations in wavelet domain.
Since the edge can be characterized by maxima of the wavelet coefficients across scales, the maxima modulus across scales are extracted. The maxima is roughly considered that it belongs to the subset of signal. And the rest of the coefficients are assumed to be the subset of noise. With this separation, the mean and variance of log normal distribution can be estimated more accurately.
Monte Carlo simulations is conducted with simulated shock waves under additive white Gaussian noise. Result shows that this the improved wavelet based shock wave detector outperforms the conventional detector, showing superiority under low SNR compared to the MSP detector .
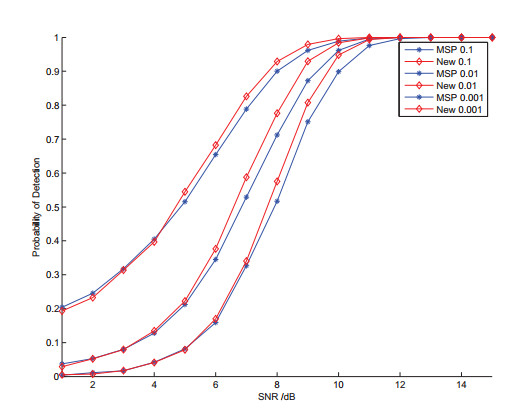
Fig. 2 Performance of detectors for method MSP (blue line) and the proposed method (red line): probability of detection versus SNRA for Pfa = 10−1,10−2,10−3 (Image by XIE).
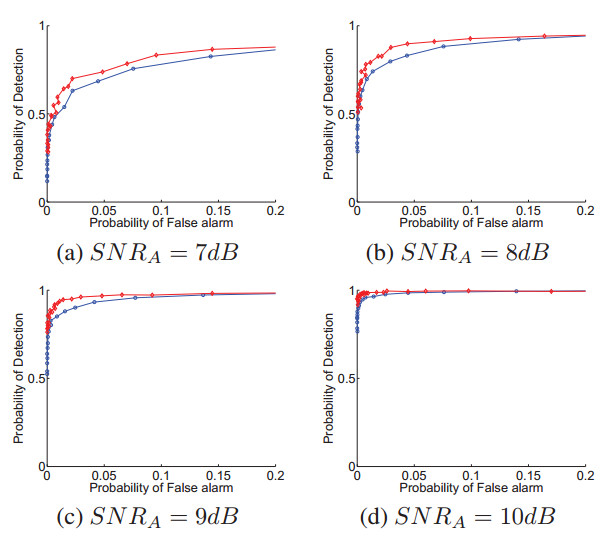
Fig. 3 ROC curves for the MSP detector(blue line) and the proposed detector(red line) (Image by XIE).
Reference:
XIE Wei, BAO Ming, LI Xiaodong and ZHANG Xiaoping. An Improved Wavelet Based Shock Wave Detector. Signal and Information Processing (ChinaSIP), 2015 IEEE China Summit and International Conference on, Chengdu, China, pp. 55 - 59, 12-15 July, 2015. DOI: 10.1109/ChinaSIP.2015.7230361
Contact:
XIE Wei
Key Laboratory of Noise and Vibration Research, Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100190 Beijing, China
Email: xiewei@mail.ioa.ac.cn


