The miniature loudspeaker is widely used in consumer electronic products. It is often used as a sub-system in applications such as hands-off telephone calls and music playing.
A smooth and flat frequency response is commonly required by telecommunication standards. Also, it is favorable for perceived sound quality.
The acoustic part of a loudspeaker system consists of the loudspeaker unit and the back cavity. When the loudspeaker unit plays sounds, the enclosure walls also vibrate and may distort the frequency response. The unwanted vibration of the enclosure wall of the loudspeaker could add to the overall acoustic output and cause distortion of the frequency response.
An experimental miniature loudspeaker model with a low-damping enclosure wall has been constructed by researchers from the Institute of Acoustics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. They investigate if there was any influence of loudspeaker wall vibration on the frequency response of the miniature loudspeaker systems.
Both an analogous circuit model and a finite element method and boundary element method model were used to calculate the enclosure wall vibration and the acoustic frequency response.
The vibration of the enclosure wall plate was simulated with an acoustical analogous circuit, in which the wall plate was modeled as a separate branch in parallel with the back cavity air volume. The acoustic frequency response of the enclosure wall was simulated with combined finite element method and boundary element method.
Simulations were validated with the vibration measurement and the acoustic frequency response measurement.
Finally, a real design model of a production type loudspeaker (Fig.1) was measured before and after modifications of the enclosure wall to show how the distortion could be reduced. Distortion up to ±15 dB on the frequency response curve had been observed around 7.8 kHz.
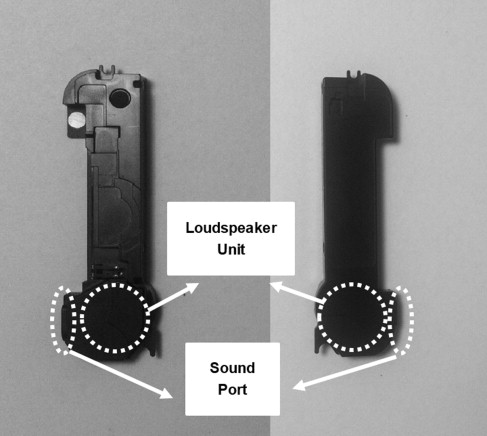
Fig.1 The front and back views of the loudspeaker module under test. The dimension of the loudspeaker module was 47 mm ∗ 12 mm ∗ 4 mm. The miniature loudspeaker unit was at one end of the enclosure case. The only sound port was on the side of the module (Image by ZHONG).
With damping material applied to the enclosure wall, the distortion was largely suppressed.
This technical note showed that the frequency response of miniature loudspeaker system could be distorted by the vibration of enclosure walls.
The analogous circuit simulation could predict the first resonant peak of the enclosure wall for simple shapes and boundary conditions.
The finite element method and boundary element method model, on the other hand, provided an estimation of all the structural modes that might affect the frequency response and the extent of the influence.
References:
ZHONG Xuan, ,WU Qunli, LI Xiaodong. Influence of Enclosure Wall Vibration on the Frequency Response of Miniature Loudspeakers. Applied Acoustics (Vol. 93, June 2015, pp. 9–14). Doi:10.1016/j.apacoust.2015.01.012
Contact:
ZHONG Xuan
Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100190 Beijing, China
Email: xuan.zhong06@gmail.com


