Keywords: HIFU; Time reversal mirror; Automatic selection
The focusing of acoustic waves in inhomogeneous media is a common and difficult problem. The focusing can be strongly degraded by sound speed variation and geometrical distortion of the array transducers. So the optimal focusing becomes very difficult to achieve.
When the target is a reflective one, the time reverse mirror, an array of transmit-receive transducers can be a solution to this problem, even when the location of the target is unknown. A first incident wave is transmitted and reflected by the target, and the received signals are stored and reversed in time, and remitted.
These procedures have an advantage in focusing a reflected target. Moreover, the iterative time reversal mirror is also used to automatically select the brightest target in a multi-target medium. A numerical simulation based on wave equation is conducted to analyze the time reversal mirror in multi-target homogeneous and tissue-like inhomogeneous media by researchers from the Institute of Acoustics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
To simulate the acoustic fields of time reversal mirror and evaluate its convergence, the FEM time-dependent model is used. An ultrasonic transducer array of 32 elements is placed at the top of the computational region as a time reversal mirror. The number of reflecting targets is more than one.
From the simulation, the position of focusing point and the pressure distribution are obtained. Three cases of time reversal process are implemented. In all three cases, it is shown that the iterative time reversal process has the ability to focus on the strongest target.
In the first iteration of the first case, the acoustic waves focus on the two targets and two lobes are observed in the plane of targets. With the number of iteration increasing, the weak lobe gradually disappears and the strong lobe remains. In the second one, the results of time reversal mirror process is similar in the tissue-like inhomogeneous medium as those in the homogeneous medium. For the third one, when three targets are very close to each other, the acoustic waves focus on the strongest target as well. Although after four iterations, the effect of iteration becomes less obvious than that in the cases of two targets, the main lobe is still much larger than the side lobes after several iterations.
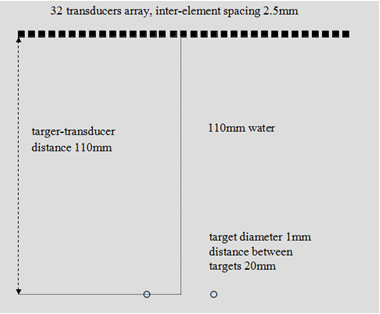
Fig. 1. Model 1. Two targets in homogenous medium (Image by PENG)
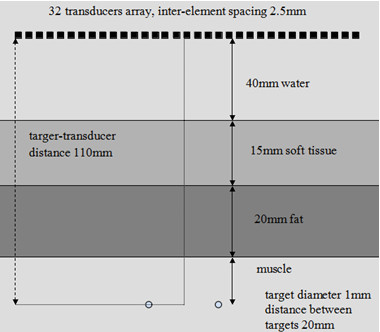
Fig.2. Model 2. Two targets in inhomogeneous medium (Image by PENG)
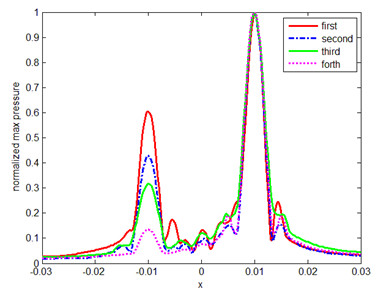
Fig. 3. Comparison of normalized pressure of each iteration in homogenous medium (Image by PENG)
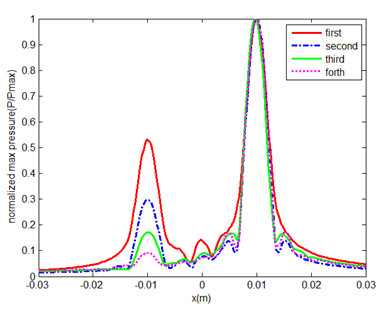
Fig. 4. Comparison of normalized pressure of each iteration in inhomogeneous medium (Image by PENG)
References:
PENG Zhefan, SU Chang, LIN Weijun. Simulation of Automatic Selection in Multi-target Medium Using Time Reversal Mirror. Piezoelectricity, Acoustic Waves, and Device Applications (SPAWDA), 2014 Symposium on, ISBN 978-1-4799-6424-6, IEEE (pp. 415-418, Oct. 30 2014-Nov. 2, 2014, Beijing, China). DOI: 10.1109/SPAWDA.2014.6998613
Contact:
PENG Zhefan
Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100190 Beijing, China
Email: zfpeng21@gmail.com


