Keywords: Surface acoustic wave, Transducers, Resonant modal, Frequency response, Phononic crystal
Interdigital transducers (IDTs), as one-dimensional (1D) phononic crystals (PnCs), have been used for many years to excite and receive surface acoustic waves (SAWs) in applications of resonators, filters and sensors. In recent years, two-dimensional (2D) PnCs obtain more attentions as they have richer properties of band gaps than 1D PnCs.
A SAW resonator with 2D reflectors which improved the Q of SAW resonator a lot had been proposed. The model of SAW resonator was analyzed based on 2D reflectors with approximating the dots by a uniform metallic layer. It adopted finite element method (FEM)/boundary element method (BEM) used in 1D IDTs. However, this method was not enough accurate when dots’ shape was ignored. As a result, more accurate calculation methods need to be explored.
A 3D FEM model to analyze the resonant modal of 2D PnCs transducers is presented. The velocity and reflectivity of per electrode are extracted, which is useful in the model of COM. The influence of the height of dots on the reflectivity of per electrode is also analyzed. These results bring references for the design of new SAW devices with the 2D PnCs transducers, which may present new challenge in the field of SAW devices.
To verify the validity of this model, the resonant modals of the 1D IDT without dots are analyzed, showing well consistency with the results of the FEM/BEM. As resonant modals in IDTs, there are two modals of SAW in the 2D PnCs transducers structure with the symmetric modal and anti-symmetric modal. As shown in Fig. 1, deformation fields of these two modals are extracted with the height of the dots 0.4 µm. Through analysis of resonant modals of different height of tungsten, velocity and the reflectivity per electrode are obtained. Fig. 2 displays the results of reflectivity with different height of tungsten dots.
The analysis results show that the 2D PnCs transducers have symmetric modal and anti-symmetric modal of SAW as the IDTs. With the increasing height of tungsten, the reflectivity per electrode has increased first and then decreased. Thus, there is an optimized height of dots for one structure with a specific 1D IDT structure to obtain high reflectivity.
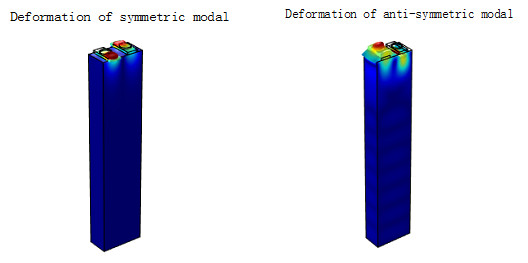
Fig.1 Deformation field of two SAW resonant modals (Image by LI).
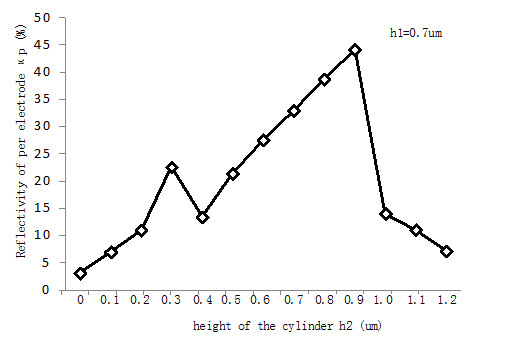
Fig.2 Y11 of transducers for IDTs and PnCs respectively (Image by LI).
References:
LI Honglang, TIAN Wenjia, TIAN Yahui, LI Xiaoxi, BAI Yongqiang, HE Shitang. Resonant Modal Analysis of the Two-dimensional Phononic Crystals Transducers. Proceedings of the 2014 Symposium on Piezoelectricity, Acoustic Waves and Device Applications. (pp. 401-403, November 2014).
Contact:
TIAN Yahui
Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100190 Beijing, China
Email: tianyahui@mail.ioa.ac.cn or yahuitian@yeah.net


