Some of the multi-channel speech enhancement (MC-SE) algorithms combine a spatial filtering with a post-filter estimator, since the amount of noise reduction by spatial filtering decreases significantly as the increasing of the reverberation time. The power-level-difference-based dual-channel post-filter (PLD-DCPF) estimator is a simple and effective way for non-stationary noise reduction. Although some improved versions have already been proposed for the PLD-DCPF estimator, its statistical properties have not been well studied until now.
Researchers from the Institute of Acoustics (IOA), Chinese Academy of Sciences have studied its statistical properties and reveal the influence of the noise power mismatch and the estimation errors of the parameters on its performance in theory. These analysis results can provide a clear path to improve the performance of this post-filter estimator.
The explicit expression of the probability density function (p.d.f.) of this post-filter estimator is derived, where a key function for this derivation is the joint p.d.f. of the auto-spectra of a two dimensional stationary Gaussian process. Using the theoretical p.d.f. expression, the impacts of the noise power mismatch and the estimation errors of the parameters on both noise reduction (NR) and speech distortion are researched. Finally, four schemes are proposed to improve the performance of the PLD-DCPF estimator based on these analysis results.
The PLD-DCPF estimator can be derived from the Wiener filter, which is given by:
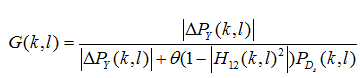
Based on the coherence function between two wide-sense stationary random processes, the p.d.f. of the PLD-DCPF estimator G(l) is given:
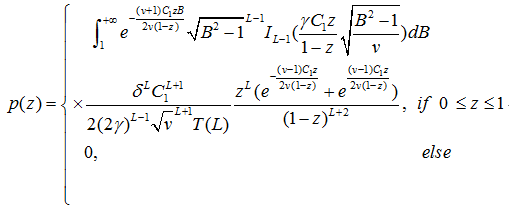
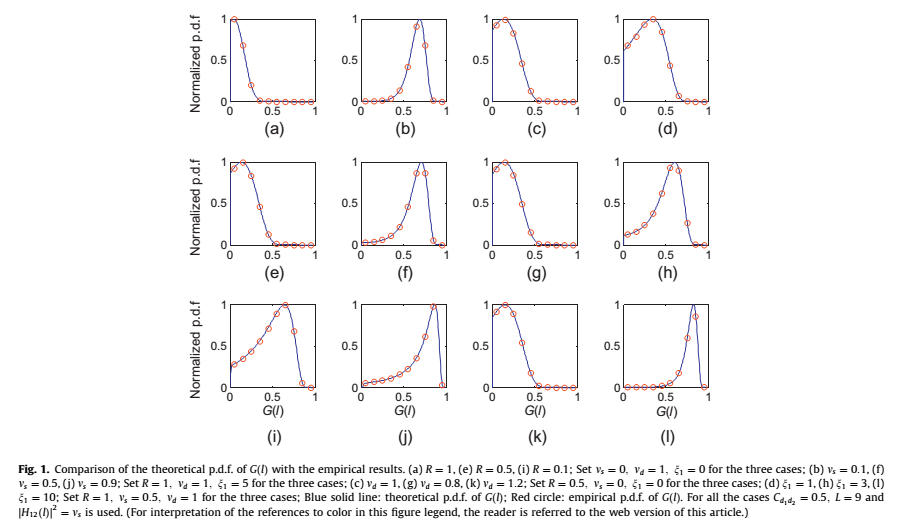
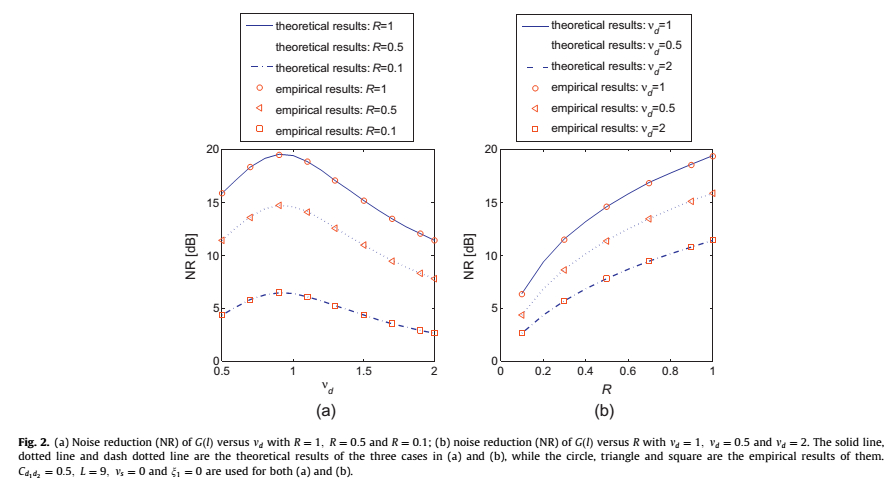
Some simulation examples show the validity of the PLD-DCPF method. The results are plotted in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2.
(Image by IOA)
Fig. 1 shows the comparison results of the theoretical p.d.f. and the empirical p.d.f. of G(l). As can be seen, the empirical results fit quite well with the theoretical results, which proves that the formula provides a good fit for the p.d.f. of G(l).
(Image by IOA)
Fig. 2(a) plots the NR versus different values of md, and Fig. 2(b) plots the NR versus different values of R. As can be seen from Fig. 2, the theoretical results fit quit well with the empirical results. Fig. 2 clearly shows the impacts of R and 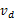 on the amount of NR.
on the amount of NR.
This research was supported in part by National Science Fund of China Under Grand Nos. 61201403 and 61302126, and also supported by the tri-networks integration under No. KGZDEW-103-5(3).
References:
WANG Shiwei, ZHENG Chengshi, PENG Renhua, LI Xiaodong. A Statistical Analysis of Power-level-difference-based Dual-channel Post-filter Estimator. Applied Acoustics (vol. 83, pp. 40-46, September 2014). DOI: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2014.02.009
Contact:
ZHENG Chengshi
Communication Acoustics Laboratory, Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100190 Beijing, China
Email: cszheng@mail.ioa.ac.cn


