Space-time adaptive processing (STAP) has been shown to be effective for clutter and jamming mitigation in airborne radar environments. Traditional STAP detectors require a large number of secondary data and excessive computation power, especially when the joint space–time dimension is large. One effective way to reduce the computational and training requirements is to model the disturbance components as a multichannel Autoregressive (AR) process and exploit it for signal detection.
However, the problem of joint adaptive parametric detection and range estimation has not been considered until now, which is the motivation of this research. Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Queens University (Canada) and ELETTRONICA S.p.A. (Italy), for the first time, investigate this problem of a small target buried in highly correlated multichannel disturbances modelled as an AR process.
To this end, it takes advantage of the target energy spillover to adjacent range samples and derives two adaptive receivers resorting to the plain generalised likelihood ratio test (GLRT) and the so-called two-step GLRT-based design procedure.
In order to estimate the disturbance covariance matrix, researchers use a set of secondary data, which is free of signal component and has the same spectral properties as the primary data. A preliminary performance assessment shows that the newly proposed detectors outperform existing solutions in open literature in terms of both probability of detection. It is carried out by means of simulated dataset, generated using multichannel AR models, and the KASSPER dataset, a widely used dataset with challenging heterogeneous effects found in real-world environments.
Moreover, the proposed methods also provide more accurate localisation within the cell under test. Further work would involve the derivation of closed-form estimate of target position for the case of moving targets, in order to reduce the computation load of the proposed detectors for on-line implementation.
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant no. 61172166.

Fig.1 Pd against SNR for the MP-GLRT, the MP-AMF, the SP-GLRT, the P-AMF and the P-RAO with simulated data; Na=4, Np= 16, K = 4, P = 2 and Pfa=10−4 (Image by HAO).
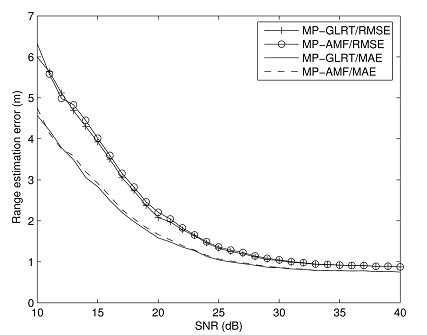
Fig.2 Range estimation error against SNR for the MP-GLRT and the MP-AMF with simulated data; Na=4, Np=16, K=4, P=2 and Pfa=10-4 (Image by HAO).
References:
HAO Chengpeng, Saeed Gazor, Danilo Orlando,Goffredo Foglia, YANG Jun. Parametric Space-time Detection and Range Estimation of a Small Target. IET Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 11p. DOI: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0081, Available online: 10 September 2014.
Contact:
HAO Chengpeng
State Key Laboratory of Acoustics, Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100190 Beijing, China


