The physicochemical properties of a chemoselective material are very critical to performance improvement in chemical sensing applications. In particular, the chemical preparation technique for sensitive films affects the coating uniformity, adhesion and quality of the sensor. As a result, many chemoselective coatings for functionalized self-assembled monolayer structures have been utilized to develop surface acoustic wave (SAW) chemical sensors that can exhibit a very rapid response at extremely low concentrations.
Lately, researchers present a novel two-step self-assembly and molecular imprinting technology for preparing sensitive films on the SAW delay line utilizing gold electrodes. It is designed for detecting organophosphorus compounds such as O-ethyl-S-2-diisopropylaminoethyl methylphosphonothiolate (VX) containing sulfur at extremely low concentrations.
First of all, mono[6-deoxy-6-[(mercaptodecamethylene) thio]]-β-cyclodextrin (Scheme 1) is chosen as the sensitive material for VX detection. And a ~2 nm-thick monolayer is formed on the SAW delay line by the binding of Au-S. This material is then analyzed by atomic force microscopy (AFM).
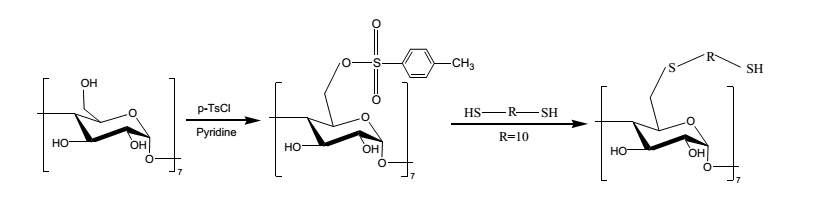
Scheme. 1 Synthesis of mono[6-deoxy-6-[(mercaptodecamethylene)thio]]-β-CD (Image by PAN).
In the following, the VX molecule is used as the template for molecular imprinting. The template is then removed by washing the delay line with ethanol and distilled water. Thereby, it produces the sensitive and selective material for VX detection.
Overall, the results indicate that mono[6-deoxy-6-[(mercaptodecamethylene)thio]]-β-CD with good chemical selectivity can be successfully designed using appropriate molecules for the formation of self-assembled, molecularly imprinted films on SAW gold delay line. It shows high sensitivity, low detection limit, and good linearity within the VX concentration of 0.15-5.8 mg/m3. The possible interactions between the film and VX are further discussed.
References:
PAN Yong, YANG Liu, MU Ning, SHAO Shengyu, WANG Wen, XIE Xiao and HE Shitang. A SAW-Based Chemical Sensor for Detecting Sulfur-Containing Organophosphorus Compounds Using a Two-Step Self-Assembly and Molecular Imprinting Technology. Sensors (Vol.14, No. 5, pp. 8810-8820, May 2014). DOI: 10.3390/s140508810


