Equalizer is widely applied in communication systems to eliminate Inter-Symbol Interference mainly caused by multipath over wireless channels. Various algorithms are developed for coefficients update of the equalizer when tracking the channel. However, advantages and drawbacks coexist for single updating algorithm.
As a result, instead of single algorithm applied in the whole frame, two algorithms, recursive least square (RLS) and least mean square (LMS), are intelligently combined in the algorithm in this research. The key idea of this algorithm is to apply RLS algorithm when the equalizer is in the convergence phase and the channel is fast varying or suffers sudden interference. Meanwhile, it switches to LMS algorithm when the equalizer already reaches to convergence and the channel is static or slowly varying. The structure of our proposed combined RLS and LMS algorithm is shown in Fig.1.
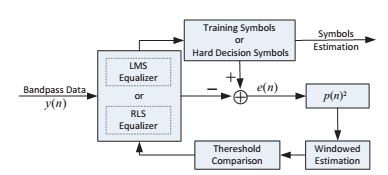
Fig. 1. The structure of the combined RLS and LMS equalizer (Image by QI).
The tackle of method is how to sense the convergence point and the channel variation. Though mean square error (MSE) tends to be stable after convergence, it is an averaged metric and cannot be utilized in a single packet. Motivated by the time-averaging autocorrelation of errors used to adjust step size, the error autocorrelation estimation is modified by smoothing it in a window to avoid frequent switch between LMS algorithm and RLS algorithm. The modified windowed autocorrelation estimation of output error e(n) and e(n-1) is proposed to track the rate of channel variation and decide whether the equalizer is in the steady state or not.
By comparing it with a pre-selected threshold in each iteration, one of RLS algorithm and LMS algorithm is chosen. Since the combined algorithm reaches to convergence using RLS algorithm, the convergence rate is fast and the length of training sequence can be decreased as a result of the effective rate increase.
Extended simulations show that the proposed combination algorithm has better MSE and bit error rate performance compared with single LMS algorithm and lower complexity compared with RLS algorithm. Moreover, the proposed algorithm can track time-varying channel with small performance degradation and dramatic complexity reduction.
The research entitled “A Combined Recursive Least Square and Least Mean Square Equalization Scheme Based on Windowed Error Autocorrelation Estimation” has been published in Image and Signal Processing (CISP), 2013 6th International Congress on (Volume:03, 16-18, Dec. 2013,pp.1462–1467).
Contact:
QI Xiaoke
Institute of Acoustics, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
Email: qixiaoke09@mails.ucas.ac.cn


