The measurement of the flow rate of gas-liquid two-phase flow has become a major focus with the development of offshore and marginal oil reserves. Many alternative methods have been tried to develop multiphase flowmeters, and several scientists had even made detailed review in multiphase flow measurement techniques.
In general, the multiphase flowmeters reported can be categorized into two types: separation measurement type and non-separation measurement type. Extracting and Separating Method (ESM), is a new generation of multiphase flowmeter which have the merits of both separation and non-separation metering method. However, the relevant devices of this method are not easy to fabricate and they have internal moving parts, which reduce reliability and increase maintenance costs.
The purpose of the present research is to report a new method and relevant device with no moving parts and is easy to fabricate. And the liquid and gas extraction ratio can be different from each other and can be regulated easily to suit the measurement condition.
As a result, a very small portion of total flow was sampled using a specially designed swirl type sampler for gas–liquid two-phase flow metering. The sampling holes were evenly placed around the circumference of the pipe wall and a swirl vane was mounted upstream to change the asymmetry flow pattern into uniform annular flow. And the total flow rate of each phase was determined according to the flow rate of sample flow and the extraction ratio. The liquid extraction ratio is mainly controlled by the number and diameter of the sampling holes and the gas extraction ratio can be obtained based on the resistance relationship between the main loop and the sample loop. Fig. 1 shows the schematic drawing of the swirl sampler developed in this research.
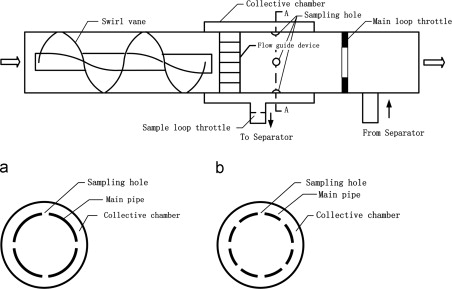
Fig. 1 Schematic drawing of the swirl sampler. (a) Sectional view A–A of 4-hole sampler and (b) sectional view A–A of 8-hole sampler (Image by LIANG).
Experiments were conducted in an air–water two-phase flow loop, flow patterns such as wavy flow, slug flow and annular flow were observed. The experimental results demonstrated that the error of flow rate measurement was less than 6.0% and independent of flow patterns. The swirl sampler has a simple structure, low capital and operational cost and which can be used widely in engineering practice.
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 51006123), Shandong Province Natural Science Foundation (Grant no. ZR2010EQ016), and State Key Laboratory of Acoustics (Grant no. SKLA201205).
The research has been published in Flow Measurement and Instrumentation (Volume 33, October 2013, Pages 145–152) with the link of http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0955598613000836.


