With the evolution of visual media, 3D video is gradually mature as a new media type for the actual application. The 3D contents can reach home via many ways, such as 3D blue-ray disk, Internet, cable TV, broadcasting and so on. Among these 3D video distribution ways, the delivery over Internet is an economical choice for 3D video home application.
With the rapid progresses in mobile networking technologies, wired Internet and mobile Internet have been fused into a unitary and heterogeneous IP-based networking environment. Facing such environment, the 3D video delivery suffers great challenges. To obtain the satisfactory 3D experience, the adaptation to networking should be considered from the perspective of source coding. For video plus depth 3D video representation, the Scalable Video Coding can be used for the 3D video streaming to provide flexible adaptations to the heterogeneous networking environments. As well, peer-to-peer (P2P) approach is an effective solution to distribute the burden of data dissemination over peers. P2P streaming also proves to be an efficient way for 3D video streaming.
Scalable 3D video P2P streaming systems can supply diverse 3D experiences for heterogeneous clients with high efficiencies. Data characteristics of the scalable 3D video make the P2P streaming efficiency more depend on the data segmentation algorithm. However, traditional data segmentation algorithm is not very appropriate for scalable 3D video P2P streaming systems. In this research, a Playback Length Changeable 3D video Segmentation (PLC3DS) algorithm is presented. It slices video and depth layers into chunks with different playback lengths. The playback length of chunk in a specified layer is determined by a length coefficient (Fig. 1), which indicates the relative playback length of the chunk.
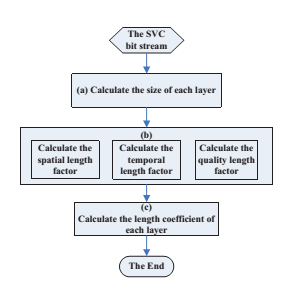
Fig. 1. The flowchart of determining the length coefficient of each layer (Image by SONG)
The research considers the specific 3D data characteristics for scalable 3D video P2P streaming system. And it provides different error resilience strengths to video and depth as well as layers with different importance levels in the transmission. The simulation results show that the proposed PLC3DS algorithm can increase the success delivery rates of chunks in more important layers, and further improve the 3D experiences of the client. Moreover, it improves the network utilization ratio remarkably.
This work was supported in part by Important National Science and Technology Specific Project under contracts 2012ZX03003006-004 and 2011ZX03005-004-02, NSFC under grant Nos.11161140319 and 61102077, Ningbo Natural Science Foundation under contract 2012A610044, and NSF under grant Nos.1145596 and 0830493.
The research result has been released online: http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6607578 and been published in Multimedia and Expo (ICME), 2013 IEEE International Conference on (pp.1-6, doi: 10.1109/ICME.2013.6607578, 15 July 2013).
Contact:
SONG Junping
High Performance Network Lab, Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing (100190), China
Email: songjp @hpnl.ac.cn


