Recently, the slow acoustic wave modes in photonic crystal (PC) have attracted much attention for its potential to design acoustic devices such as delay lines, filters and resonators. Many researchers and scientists are now trying to design these unconventional devices.
Researchers from the Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences have also designed a PCplate for slow acoustic wave.They numericallyinvestigated the propagation of Lamb waves in a two-layered free standing plateby the finiteelement method. And the plate was composed of a one-dimensional photoniccrystal thin layer coated on uniform substrates of different thicknesses.
The investigation is an acoustic analog of the much studied optical phenomenon of slow light propagation. The numerical analysis of the investigation demonstrates that the variation of thickness of the substrate leads to obvious changes in the dispersion curves of the Lamb waves and the widths of the band gaps. And the group velocity of certain branch could be tuned from the positive to the negative, which is shown in Fig 1. Moreover, a nearly flat band with very slow group velocities which did not exist in the complete band gap of perforate plates on the substrate is found. For a better understanding of the flat band, they present a brief investigation and show that the flat band is caused by the interaction of the vibration modes of the thin plate above the hole with the Bloch modes of the PC plate. The group velocities in this mode are very slow and slightly change with the thickness of the substrate. In addition, compared to the PC plate with no substrate, the extreme of the group velocity of PC plate with thin substrate decreases more than half and increases with the thickness. The results reveal potential applications in design of new acoustic devices.
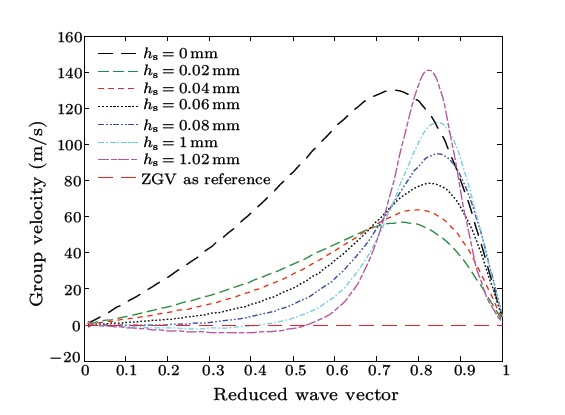
Fig.1. The group velocities of the flat band when the substrate thickness increases (Image by ZHANG).
The research titled “Numerical Investigation of the Slow Acoustic Wave Modes in a One-Dimensional Phononic Crystal Plate” was released online http://cpl.iphy.ac.cn/EN/Y2013/V30/I8/086301 and on CHIN. PHYS. LETT (Vol.30, No.8, June 2013, Page 086301, 3 Pages).
Contact:
ZHANG Xu
Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190
Email: zhangxu210@mail.ioa.ac.cn


