In the sonar system, reverberation has always been the interference that is expected to be suppressed. For the underwater mobile sonar platform, due to its own movement, the reverberation space-time spectrum may expand in the two-dimensional plane and has the property of space-time coupling, which would make trouble to the reverberation suppression.
STAP (Space Time Adaptive Processing) is an effective method to suppress space-time coupling reverberation. However, to apply STAP in the underwater environment, two problems need to be solved. First of all, the underwater environment is complex and the samples of available uniform auxiliary data are seriously insufficient. Secondly, even if there are enough independent samples of the same distribution, fully adaptive STAP requires the inverse of the high-dimensional matrix, which generates a large amount of computation.
In order to solve the above difficulties, researchers from the Institute of Acoustics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IACAS) proposed a joint domain localized dimensionality reduced-dimension STAP method utilizing array symmetry characteristics. The method is able to reduce computational cost and improve the performance of reverberation suppression in the limited samples.
The research was published in the international journal The Journal of Engineering.
The researchers studied the structure of reverberation covariance matrix, discovered the properties of persymmetry. By combining it with JDL-STAP, they proposed a Per-JDL algorithm based on prior knowledge.
The results showed that when there were enough training samples, the performance loss of JDL STAP compared with the optimal STAP was 6dB, while Per-JDL STAP compared with the optimal STAP was 4dB.When the training samples were insufficient, the performance loss of JDL STAP algorithm was 25dB, while that of Per-JDL STAP algorithm was 6dB.
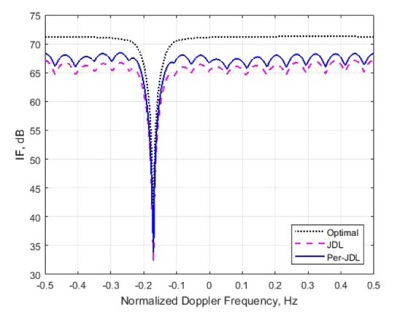
Figure 1. Comparison of algorithm performance when the training samples were sufficient. (Image by IOA)
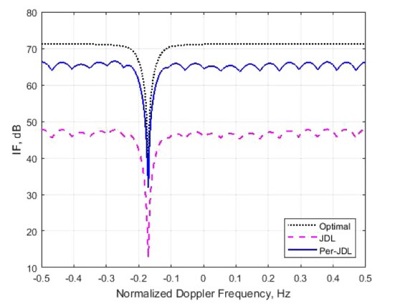
Figure 2. Comparison of algorithm performance when the training samples were insufficient. (Image by IOA)
The algorithm maximized the use of training samples, greatly reduced the computation complexity, and improved the performance of interference suppression. Therefore, this method has a good application prospect in the underwater mobile platform. Next, the researchers will further verify the advantages of the method in practical application and further improve the performance of the algorithm.
The research was supported by National Natural Science Foundationof China under Grants No. 61701490.
Reference:
WANG Sha, SHI Bo, HAO Chengpeng, LIU Minggang, XU Da. Exploiting persymmetry for JDL-STAP. IET International Radar Conference, The Journal of Engineering, Vol. 2019, Iss. 19, pp. 6113-6116. DOI: 10.1049/joe.2019.0204
Contact:
ZHOU Wenjia
Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100190 Beijing, China
E-mail: media@mail.ioa.ac.cn